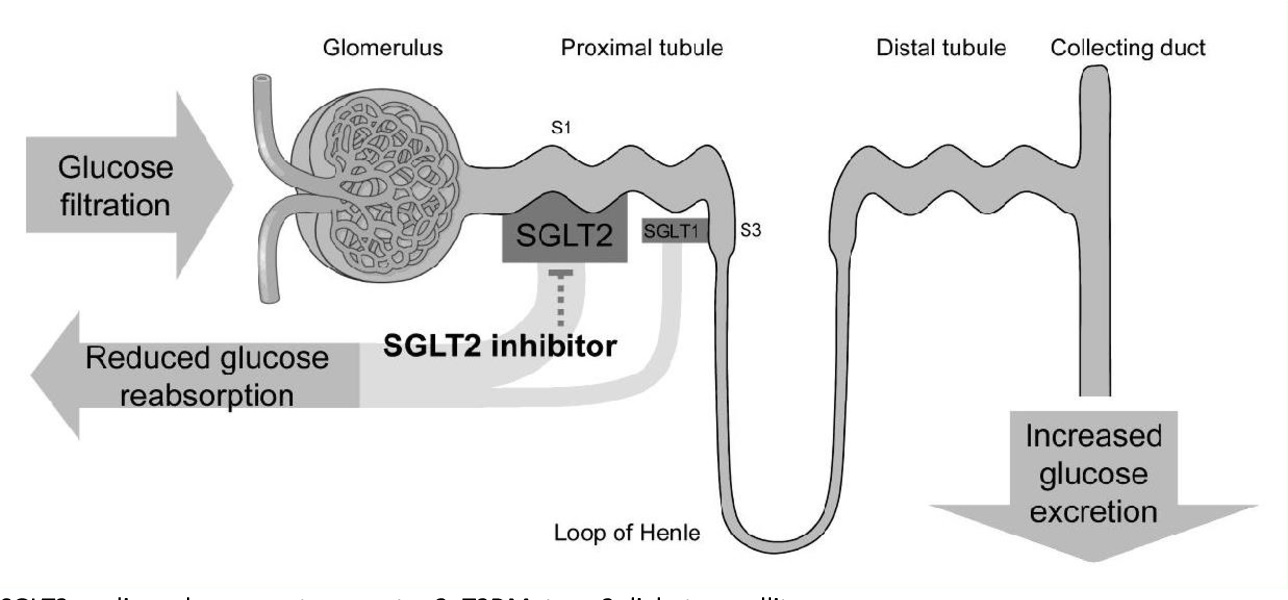
SGLT2 inhibitors, otherwise known as Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 inhibitors, are a class of prescription drugs notably employed in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The primary function of SGLT2 inhibitors is to lower blood sugar levels by blocking the function of SGLT2 proteins, thereby forcing the kidneys to excrete more glucose through urine. The application of SGLT2 inhibitors presents an alternative method to diabetic care by which glucose management and cardiovascular risk reduction are merged into one healthcare consideration. This principle is at the core of Border Free Health, where drugs like SGLT2 inhibitors are utilized as part of holistic health plans.
At their core, SGLT2 inhibitors decrease the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, thereby raising the amount of glucose excreted through urination. This, in turn, leads to a reduction of glucose levels in the bloodstream. Notably, the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors is independent of insulin, making these drugs particularly beneficial for patients with insulin resistance or deficiency.
Cardiovascular and Renal Benefits
Apart from their fundamental use in glucose control, SGLT2 inhibitors have recently been noted for their cardiovascular and renal benefits. Major clinical trials have shown that this class of drugs may considerably reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure and progression of kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, they have been associated with blood pressure reduction and weight loss, both advantageous for cardiovascular health.
Notably, these benefits have been observed even in patients without diabetes, expanding the potential therapeutic uses of SGLT2 inhibitors. Therefore, a diversified range of patients could potentially benefit. At A wide range of prescription medication, SGLT2 inhibitors are among the medicines offered to treat various conditions.
While the specific mechanisms underlying these benefits are not yet fully understood, it is believed that the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart and kidney function may be linked to their ability to reduce blood glucose levels, lower blood pressure, and reduce weight.
It’s crucial for those considering invoking this drug class into their treatment plans to also consider potential side effects. Commonly noted adverse effects include urinary tract infections, increased urination, and a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis (a serious diabetes-related complication).
Innovative healthcare approaches like https://borderfreehealth.com/ provide platforms to explore SGLT2 inhibitors and other state-of-the-art treatment options for various conditions. It is always recommended for individuals to consult their healthcare providers before making any changes to their medication regime. Experimenting, learning, and finding the best practices is key to ensuring optimal healthcare management.

 Utilizing 3d printing technology in medical training
Utilizing 3d printing technology in medical training  Online THC A Flowers: Best Options Available
Online THC A Flowers: Best Options Available  Entails of terpenes in Delta 8 gummies
Entails of terpenes in Delta 8 gummies  Why are regular check-ups with a thyroid health specialist important?
Why are regular check-ups with a thyroid health specialist important?  Pain Down There? You Are Not Alone! Understanding Chronic Pelvic Pain
Pain Down There? You Are Not Alone! Understanding Chronic Pelvic Pain  What Allied Health Services are Available in Werribee for NDIS Participants?
What Allied Health Services are Available in Werribee for NDIS Participants?  What to Expect When Visiting a Pain Center for the First Time?
What to Expect When Visiting a Pain Center for the First Time?  Health benefits of using the best magic mushroom gummies
Health benefits of using the best magic mushroom gummies  Addiction is a complex and devastating disease.
Addiction is a complex and devastating disease.