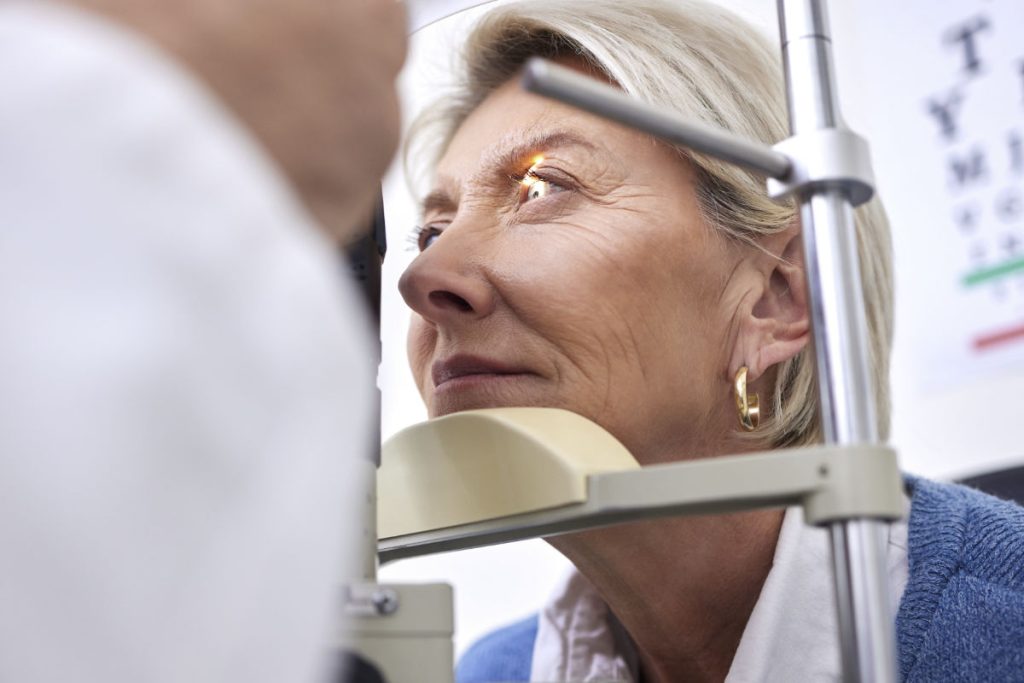
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of vision loss among people with diabetes. This condition occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the small blood vessels in the retina, leading to swelling, leakage, or abnormal blood vessel growth.
Without proper management, diabetic retinopathy can progress to severe vision impairment or even blindness. Fortunately, advancements in diabetic eye disease treatment have provided several effective options for managing this condition and slowing its progression.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Stages of the Disease
Diabetic retinopathy develops in stages:
- Mild Non-Proliferative Retinopathy: Small areas of swelling in the blood vessels (microaneurysms) appear, leading to minor leakage.
- Moderate Non-Proliferative Retinopathy: More blood vessels become blocked, reducing oxygen supply to the retina.
- Severe Non-Proliferative Retinopathy: More significant blockage occurs, prompting the retina to create new, fragile blood vessels.
- Proliferative Retinopathy: The most advanced stage, where abnormal blood vessels grow in the retina, leading to bleeding, scarring, and retinal detachment.
Early detection through regular eye exams is crucial in preventing severe complications.
Best Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
1. Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure Management
The foundation of treating diabetic retinopathy starts with controlling diabetes itself. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels through proper diet, exercise, and medication can slow disease progression. High blood pressure also worsens the condition, so keeping it in check with lifestyle changes or medication is essential.
2. Anti-VEGF Injections
One of the most effective treatments for diabetic macular edema (DME), a complication of diabetic retinopathy, is anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapy. Drugs such as ranibizumab, aflibercept, and bevacizumab are injected into the eye to reduce swelling and prevent new blood vessel growth. Many patients experience improved vision and reduced disease progression with this treatment.
3. Laser Therapy (Photocoagulation)
Laser treatment is another common approach for managing diabetic retinopathy. There are two main types:
- Focal Laser Treatment: Targets specific leaking blood vessels to prevent fluid buildup.
- Panretinal Photocoagulation (PRP): Treats a larger area of the retina to shrink abnormal blood vessels and prevent further damage.
Laser therapy helps slow vision loss, but it is most effective when performed in the early to middle stages of the disease.
4. Steroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections, such as dexamethasone implants, can help reduce inflammation and swelling in the retina. These treatments are often used in combination with other therapies, like anti-VEGF injections, for better results. However, steroid use may increase the risk of cataracts and glaucoma, requiring careful monitoring by an eye specialist.
5. Vitrectomy Surgery
In very advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy, where there is severe bleeding (vitreous hemorrhage) or retinal detachment, vitrectomy surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the blood-filled vitreous gel and replacing it with a clear solution to restore vision. Vitrectomy may be a sight saving surgery in advanced disease.
Emerging Treatments and Future Innovations
Gene Therapy and Stem Cell Research
Research is ongoing to explore gene therapy and stem cell-based treatments for diabetic retinopathy. These approaches aim to repair damaged retinal cells and improve blood vessel function, offering potential long-term solutions for vision preservation.
Artificial Intelligence in Eye Care
AI-driven retinal screening tools are improving early detection and monitoring of diabetic retinopathy. These advancements allow for quicker diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, enhancing patient outcomes.
Choosing the Right Diabetic Eye Disease Treatment
Factors to Consider
The best treatment approach depends on several factors, including the stage of the disease, overall health, and response to initial treatments. Some patients may benefit from a combination of therapies, such as anti-VEGF injections followed by laser treatment.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Since diabetic retinopathy can develop without noticeable symptoms in its early stages, routine eye exams are critical. Eye specialists can detect changes in the retina before significant vision loss occurs and recommend timely interventions.
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious but manageable condition with the right treatment approach. From lifestyle modifications and medications to advanced therapies like anti-VEGF injections and laser treatment, there are multiple ways to slow disease progression and protect vision. Consulting an eye specialist for regular screenings and timely diabetic eye disease treatment is essential for maintaining eye health and preventing complications.

 Nutrition and Healing in Sarcoma Recovery: Dental Health, Treatment Plans, and Whole-Body Care
Nutrition and Healing in Sarcoma Recovery: Dental Health, Treatment Plans, and Whole-Body Care  Inside the HRT Clinic: How Hormones Influence Weight, Stress, and Cardiovascular Health
Inside the HRT Clinic: How Hormones Influence Weight, Stress, and Cardiovascular Health  Eye Bag Removal: Your Guide to Looking Fresh Every Day
Eye Bag Removal: Your Guide to Looking Fresh Every Day  Transitioning from Maternity to Workplace Wellness
Transitioning from Maternity to Workplace Wellness  Aging Gracefully: How Hearing Care and Home Support Improve Daily Living
Aging Gracefully: How Hearing Care and Home Support Improve Daily Living  The Role of Routine and Structure in Child Development
The Role of Routine and Structure in Child Development  Restoring Confidence Through Advanced Facial Procedures
Restoring Confidence Through Advanced Facial Procedures  Autism Therapy Programs Supporting Communication and Social Developments
Autism Therapy Programs Supporting Communication and Social Developments  From Burnout To Balance: How Weight, Motherhood, And Heart Health Intersect
From Burnout To Balance: How Weight, Motherhood, And Heart Health Intersect