Embarking on a fitness journey can feel daunting, especially with the pressure of gym memberships and specialized equipment. However, the truth is, you don’t need any of that to begin building strength and improving your overall health. Bodyweight exercises are a fantastic starting point, offering a convenient and effective way to engage your muscles and enhance your fitness levels right in the comfort of your home. These exercises utilize your own body weight as resistance, making them accessible to beginners of all fitness levels.
Mastering Foundational Movements
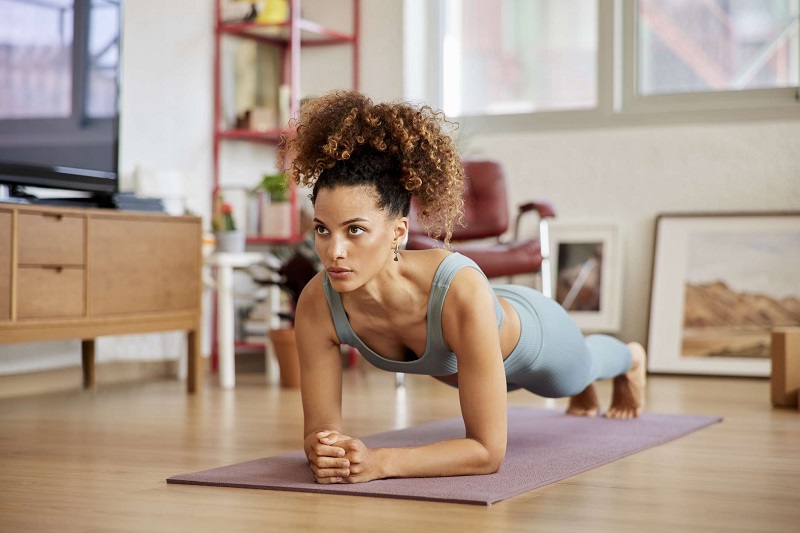
The key to a successful bodyweight workout lies in mastering fundamental movements. Squats, for instance, are a cornerstone exercise that targets your quads, glutes, and hamstrings. Remember to keep your back straight, chest up, and descend as if you’re sitting into a chair. Push-ups, another classic, engage your chest, shoulders, and triceps. If full push-ups are challenging, start with modified push-ups on your knees. Planks are excellent for core strengthening. Hold a straight line from head to heels, engaging your abs and glutes, and gradually increase the duration of your hold. These three exercises form a solid foundation for building strength and stability. Knowing the workout tips for beginners would be essential also.
Adding Variety for a Full-Body Workout
Building upon foundational exercises, incorporating variety is key to a comprehensive and effective workout routine. Lunges, a dynamic exercise, are excellent for engaging your leg muscles and glutes while simultaneously enhancing balance and coordination. For an added challenge, try incorporating walking lunges to further engage your muscles. To target your abdominal muscles and build a stronger core, integrate crunches and Russian twists into your routine. These exercises work different aspects of your abdominal region, contributing to overall core strength and stability. Focusing on your posterior chain, Superman exercises are ideal for strengthening your lower back. This exercise involves lifting your arms and legs simultaneously while lying on your stomach, promoting back health and stability. By including these variations, you’ll ensure a well-rounded workout that effectively targets all major muscle groups for optimal fitness.
Progressive Overload and Proper Form
As you get stronger, it’s crucial to progressively overload your muscles to continue seeing results. This can be achieved by increasing the number of repetitions, sets, or the difficulty of the exercise. For example, you can transition from knee push-ups to full push-ups. However, always prioritize proper form over quantity. Maintaining good form ensures that you’re targeting the correct muscles and minimizing the risk of injury. If you’re unsure about your form, consider watching videos or consulting with a fitness professional for guidance.
Consistent Effort for Lasting Results
The beauty of bodyweight exercises lies in their accessibility. You can do them anywhere, anytime, making it easier to incorporate them into your daily routine. Consistency is key when it comes to fitness. Aim for at least three bodyweight workouts per week, allowing for rest days in between. Start with a warm-up, such as light cardio and dynamic stretching, and end with a cool-down, including static stretching. With dedication and consistent effort, you’ll be amazed at the progress you can make with these simple yet effective no-equipment exercises.