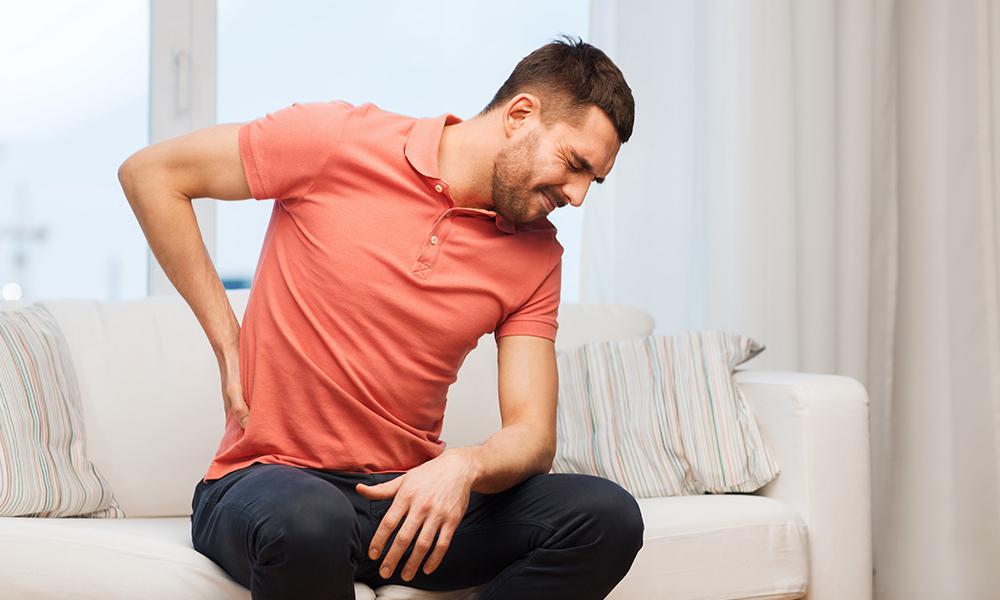
Back pain is a prevalent issue that affects millions of people worldwide, impacting their daily lives and overall well-being. From mild discomfort to debilitating agony, back pain can vary widely in its severity and manifestations. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effectively managing this common ailment.
Causes of Back Pain
- Muscle Strain: One of the most common causes of back pain is muscle strain or injury, often resulting from sudden movements, lifting heavy objects improperly, or poor posture.
- Herniated Discs: When the soft inner material of a spinal disc protrudes through its tough exterior, it can irritate nearby nerves, leading to back pain.
- Degenerative Conditions: Conditions such as osteoarthritis and degenerative disc disease can cause the breakdown of spinal discs and joints, contributing to chronic back pain.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, causing pain, numbness, and weakness in the back and legs.
- Traumatic Injuries: Accidents, falls, or trauma to the spine can result in fractures, dislocations, or other injuries leading to back pain.
Symptoms of Back Pain
- Dull Aching: Persistent, dull aching in the back region, which may worsen with movement or certain activities.
- Sharp or Shooting Pain: Intense, shooting pain that radiates from the back to the buttocks, legs, or feet, often indicative of nerve compression or irritation.
- Muscle Stiffness: Tightness or stiffness in the muscles of the back, making it difficult to move or bend comfortably.
- Limited Mobility: Reduced range of motion in the back, accompanied by difficulty in performing daily tasks or activities.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or weakness in the back or extremities, suggesting nerve involvement.
Treatment Options
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate mild to moderate back pain. In cases of severe pain, prescription medications or muscle relaxants may be prescribed.
Physical Therapy
Targeted exercises, stretching routines, and manual therapy techniques can strengthen the muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate back pain.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat packs or cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce inflammation, soothe sore muscles, and relieve pain.
Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing can help prevent back pain or reduce its severity.
Surgical Intervention
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical procedures such as spinal decompression, fusion, or disc replacement may be recommended.
The Role of Knee Replacement in Back Pain
While knee replacement surgery primarily addresses issues related to knee joint degeneration and arthritis, its impact on back pain should not be underestimated. Oftentimes, individuals with knee problems compensate for their discomfort by altering their gait or posture, which can place added stress on the back and contribute to back pain. By restoring proper function and mobility to the knee joint through replacement surgery, patients may experience improved overall biomechanics, leading to reduced strain on the back and decreased back pain.
Conclusion
Back pain can significantly diminish one’s quality of life, but with proper understanding and management, its impact can be minimized. By addressing underlying causes, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and exploring various treatment modalities, individuals can find relief from back pain and regain control over their daily activities. Whether through conservative measures or surgical intervention, seeking timely medical attention is key to effectively managing back pain and promoting long-term spinal health.

 Eye Bag Removal: Your Guide to Looking Fresh Every Day
Eye Bag Removal: Your Guide to Looking Fresh Every Day  Transitioning from Maternity to Workplace Wellness
Transitioning from Maternity to Workplace Wellness  Aging Gracefully: How Hearing Care and Home Support Improve Daily Living
Aging Gracefully: How Hearing Care and Home Support Improve Daily Living  The Role of Routine and Structure in Child Development
The Role of Routine and Structure in Child Development  Restoring Confidence Through Advanced Facial Procedures
Restoring Confidence Through Advanced Facial Procedures  Autism Therapy Programs Supporting Communication and Social Developments
Autism Therapy Programs Supporting Communication and Social Developments  From Burnout To Balance: How Weight, Motherhood, And Heart Health Intersect
From Burnout To Balance: How Weight, Motherhood, And Heart Health Intersect  Significance Of FUT+FUE+BHT Combine Technique & How Is It Done?
Significance Of FUT+FUE+BHT Combine Technique & How Is It Done?  Lifestyle Changes That Could Help Lessen the Effects of Alzheimer’s
Lifestyle Changes That Could Help Lessen the Effects of Alzheimer’s 