Mouse models have revolutionized biomedical research, enabling scientists to study various human diseases and their underlying mechanisms in a controlled environment. Among these models, the B6-Dmd Del52 mouse model has emerged as a powerful tool for investigating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a debilitating genetic disorder affecting muscle strength and function. In this article, we delve into the significance of B6-Dmd Del52 in understanding DMD and shed light on how this mouse model contributes to the development of potential therapeutic interventions.
Understanding B6-Dmd Del52:
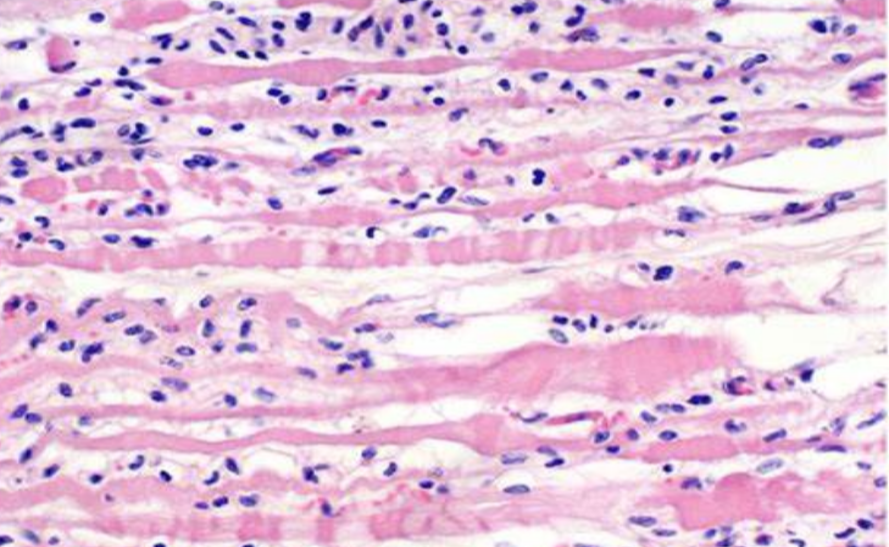
B6-Dmd Del52 is a genetically engineered mouse model designed to mimic a specific mutation found in human DMD patients. Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, resulting in the absence or dysfunctional production of the dystrophin protein. The B6-Dmd Del52 mouse model carries a deletion of 52 exons in the dystrophin gene, causing a frameshift mutation that disrupts the reading frame and renders the protein non-functional. This mutation closely resembles the condition observed in DMD patients, making the B6-Dmd Del52 mouse an excellent representation of the disease.
Phenotypic Resemblance and Disease Progression:
One of the key advantages of the B6-Dmd Del52 mouse model is its phenotypic resemblance to human DMD. These mice display similar muscle weakness, wasting, and impaired locomotion observed in DMD patients. Furthermore, the B6-Dmd Del52 model exhibits a progressive disease course, which mirrors the gradual deterioration seen in humans with DMD. This allows researchers to track disease progression over time, facilitating a better understanding of the underlying pathological processes.
Exploring Disease Mechanisms:
The B6-Dmd Del52 mouse model serves as a valuable tool for unraveling the complex molecular mechanisms underlying DMD. By studying these mice, researchers can investigate how the absence of functional dystrophin affects muscle physiology, leading to muscle degeneration and weakness. They can examine the interactions between dystrophin and other proteins involved in muscle contraction and membrane stability. Furthermore, the B6-Dmd Del52 model enables investigations into the downstream effects of dystrophin deficiency, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and impaired regeneration processes.
Evaluating Therapeutic Interventions:
The availability of the B6-Dmd Del52 mouse model has significantly contributed to the development and evaluation of potential therapeutic interventions for DMD. Researchers can utilize these mice to test novel drugs, gene therapies, and other treatment strategies. By assessing the effects of interventions on disease progression, muscle function, and survival in the B6-Dmd Del52 model, scientists can gain critical insights into the potential efficacy and safety of these therapeutic approaches. This helps to inform the design and optimization of clinical trials in humans, ultimately advancing the field of DMD research.
Translational Potential:
The findings obtained from B6-Dmd Del52 mouse studies have direct translational potential, aiding in the development of therapeutic strategies for DMD patients. Researchers can identify promising interventions based on their effects in the B6-Dmd Del52 model and further investigate their efficacy and safety in preclinical studies. By bridging the gap between preclinical research and clinical applications, the B6-Dmd Del52 model accelerates the translation of scientific discoveries into potential treatments for DMD.
Collaborative Research and Future Directions:
The B6-Dmd Del52 mouse model has facilitated collaborative research efforts, bringing together scientists, clinicians, and industry partners. Collaborations allow for a multidisciplinary approach to DMD research, enabling the exploration of diverse therapeutic modalities and innovative strategies. Additionally, the insights gained from the B6-Dmd Del 52 model can guide the development of improved mouse models, incorporating additional genetic modifications or specific cell types, to further enhance our understanding of DMD.
Conclusion:
The B6-Dmd Del52 mouse model has emerged as an invaluable resource in the field of DMD research, shedding light on disease mechanisms and driving the development of potential therapeutic interventions. Through its phenotypic resemblance, disease progression, and the ability to evaluate various interventions, this model accelerates the translation of discoveries into clinical applications. As collaborative research continues to thrive, and with ongoing advancements in mouse modeling techniques, the future holds promising possibilities for unraveling the complexities of DMD and improving the lives of those affected by this devastating disorder.